Heat Pump or Air Conditioner? Understanding the Key Differences
When it comes to choosing the right cooling system for your home, understanding the key differences between a heat pump and an air conditioner is crucial. While both options provide relief from the scorching heat, they operate in distinct ways and offer their unique advantages.
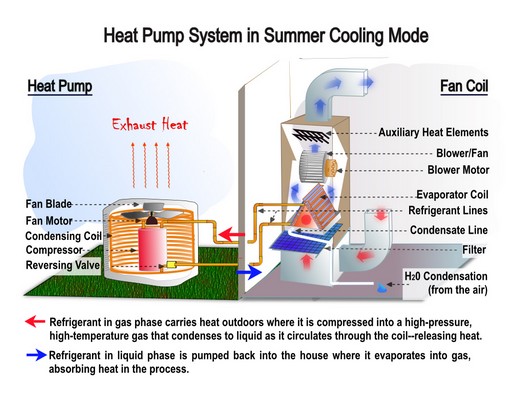
An air conditioner operates by removing heat from the indoor air and expelling it outside, keeping your home cool and comfortable. On the other hand, a heat pump can both cool and heat your home by transferring heat from one place to another. This means that during the colder months, a heat pump can be a cost-effective solution for efficient heating as well.
One of the primary differences between a heat pump and an air conditioner lies in their energy efficiency. Heat pumps are known for their remarkable efficiency, as they transfer heat rather than generate it. This translates to lower energy bills and a reduced carbon footprint. However, it’s important to note that the efficiency of a heat pump decreases as the outdoor temperature drops.
Another crucial difference is the installation process. While air conditioners are typically easier and cheaper to install, heat pumps require a more complex process due to their dual functionality. Additionally, the availability of fuel sources can impact your decision. Air conditioners primarily rely on electricity, while heat pumps can utilize electricity, natural gas, or oil as their energy source.
In conclusion, understanding the key differences between a heat pump and an air conditioner is essential in making an informed decision for your home’s cooling solution. Consider factors such as energy efficiency, installation requirements, and the availability of fuel sources to determine which option best suits your needs. Whether you opt for the versatility of a heat pump or the simplicity of an air conditioner, both systems can provide the cool relief you seek during the hot summer months.
Heat Pump or Air Conditioner: Which is the Right Cooling Solution for Your Home?
When it comes to cooling your home, there are two primary options: a heat pump and an air conditioner. While they both serve the same purpose of cooling your living space, there are key differences between the two that you need to be aware of before making a decision.
| Function | A heat pump can both cool and heat your home. It functions by transferring heat from one location to another using refrigerant. | An air conditioner is designed solely for cooling purposes. It removes heat from the indoor air and releases it outside. |
| Efficiency | A heat pump is generally more energy-efficient compared to an air conditioner. Since it can also be used for heating, it can provide both cooling and heating needs with less energy consumption. | An air conditioner is typically less efficient, as it only serves the purpose of cooling. It requires a separate heating system if heating is needed. |
| Climate Suitability | A heat pump is ideal for moderate climates where both cooling and heating needs are required throughout the year. | An air conditioner is suitable for hot climates where cooling needs are predominant, and heating is not a major concern. |
| Cost | A heat pump tends to have a higher upfront cost compared to an air conditioner due to the dual functionality it provides. | An air conditioner is usually more affordable in terms of upfront cost. |
In summary, the choice between a heat pump and an air conditioner depends on your specific needs and circumstances. If you live in a moderate climate and require both cooling and heating, a heat pump may be the right choice for you. However, if you live in a hot climate and heating is not a concern, an air conditioner can be a more cost-effective option. Consider factors such as efficiency, climate suitability, and cost to make an informed decision for your home cooling solution.
Functionality and Operation
Understanding the functionality and operation of a heat pump and air conditioner is key to identifying the differences between these cooling solutions. While both devices serve the purpose of cooling the air in your home, they function in different ways.
An air conditioner operates by removing heat from the air inside your home and releasing it outside. It uses refrigerant to absorb heat from the indoor air, and then transfers it to the outdoor unit, where it is expelled. This process cools the air inside your home, making it more comfortable.
A heat pump, on the other hand, can both cool and heat your home. It works by transferring heat from one place to another using a refrigerant. In the summer, it removes heat from the indoor air and releases it outside, similar to an air conditioner. In the winter, it reverses the process by drawing heat from the outside air and bringing it inside, warming your home.
One of the key differences between a heat pump and an air conditioner is that a heat pump can provide heating in addition to cooling. This makes it a more versatile and energy-efficient option, as it can be used year-round to maintain a comfortable indoor temperature.
Another difference is that a heat pump can be more expensive to install than an air conditioner, as it requires additional components and capabilities. However, the long-term energy savings and the ability to provide both heating and cooling can make it a cost-effective choice over time.
In summary, understanding the functionality and operation of a heat pump and air conditioner is essential in determining which cooling solution is best suited for your home. While both devices cool the air, a heat pump has the advantage of also providing heating, making it a versatile and energy-efficient option.
Efficiency and Energy Consumption
When comparing a heat pump and an air conditioner, one of the key differences lies in their efficiency and energy consumption. It’s important to understand how these cooling solutions work to make an informed decision for your home.
A heat pump operates by transferring heat from one area to another, using refrigerant to absorb and release heat. This means that it can provide both heating and cooling functions, which makes it highly efficient. By using the same system for both heating and cooling, it reduces the amount of energy needed, making it a more cost-effective option.
On the other hand, an air conditioner cools the air by removing heat and humidity from the indoor space. It does not have the ability to provide heating, so it is solely focused on cooling. This makes it less versatile than a heat pump, but it can still be an effective cooling solution for your home.
When it comes to energy consumption, heat pumps generally consume less energy compared to traditional air conditioners. This is because they transfer heat instead of generating it, which requires less energy input. Heat pumps can be up to 50% more efficient than air conditioners, resulting in significant energy savings over time.
Additionally, heat pumps also have the advantage of using renewable energy sources. They can be powered by electricity generated from solar panels or wind turbines, further reducing their carbon footprint. This makes them a greener option for cooling your home.
In conclusion, the efficiency and energy consumption of a heat pump and an air conditioner differ significantly. By understanding the key differences between these cooling solutions, you can choose the best option for your home based on your specific needs and priorities.
Cooling Capacity and Output
When it comes to cooling capacity and output, there are key differences between a heat pump and an air conditioner. Understanding these differences can help you make an informed decision about which cooling solution is right for your home.
Air Conditioners:
An air conditioner is designed solely for cooling purposes. It extracts heat from the indoor air and transfers it outside, resulting in cooler air inside your home. Air conditioners are typically rated in terms of their cooling capacity, which is measured in British Thermal Units (BTUs) per hour. The cooling capacity of an air conditioner indicates how much heat it can remove from the air in a given period of time. The higher the cooling capacity, the more cooling power the air conditioner has.
Heat Pumps:
A heat pump, on the other hand, can both heat and cool your home. It operates by extracting heat from the outdoor air and transferring it indoors during colder months, and vice versa during hotter months. Heat pumps are also rated in terms of their cooling capacity, measured in BTUs per hour. However, the cooling capacity of a heat pump is generally lower compared to that of an air conditioner. This is because a heat pump is designed to provide a balanced temperature, rather than solely focusing on cooling.
In summary, while both a heat pump and an air conditioner can provide cooling, their cooling capacities and outputs differ. An air conditioner is dedicated to cooling and has a higher cooling capacity, while a heat pump is designed for both heating and cooling, with a typically lower cooling capacity. Understanding these differences can help you choose the right cooling solution for your home.
Heating Capability
Understanding the key differences between an air conditioner and a heat pump starts with their heating capabilities.
An air conditioner functions primarily as a cooling system, designed to remove heat from an indoor space and expel it outside. It does not have the ability to generate heat on its own.
On the other hand, a heat pump is a versatile device that can provide both cooling and heating. It operates by utilizing a refrigeration cycle to transfer heat between the indoors and outdoors. During the colder months, heat pumps can extract heat from the outside air (even in cooler temperatures) and distribute it inside to warm the space.
By offering both heating and cooling capabilities, heat pumps provide a year-round solution for climate control in a home. This dual function makes heat pumps a more efficient and cost-effective option compared to relying solely on an air conditioner for cooling and a separate heating system for the colder months.
Climate Compatibility
Understanding the climate in which you live is key when determining whether a heat pump or an air conditioner is the right cooling solution for your home. Both options have their strengths and weaknesses, making it important to consider the specific demands of your climate.
A heat pump is designed to operate efficiently in moderate climates, where the temperature range typically stays above freezing. This is because a heat pump uses the outside air as a heat source, meaning it extracts heat from the air and transfers it into your home. In colder climates, where temperatures often drop below freezing, the heat pump may struggle to extract enough heat from the air, resulting in decreased efficiency and potential system damage.
On the other hand, an air conditioner is better suited for hotter climates, where the demand for cooling is high. An air conditioner works by removing heat from the indoor air and venting it outside. In regions with hot and humid summers, air conditioners can provide powerful cooling and dehumidification, making them an ideal choice for maintaining comfort in these climates.
Overall, understanding the specific climate compatibility of a heat pump or an air conditioner is crucial in determining which cooling solution is right for your home. Consulting with a professional HVAC technician can help you make an informed decision based on the unique characteristics of your climate and your cooling needs.
Installation Requirements
Understanding the key differences between a heat pump and an air conditioner is crucial when it comes to deciding which one is the best cooling solution for your home. One key difference lies in their installation requirements.
A heat pump requires a professional installation, as it involves both indoor and outdoor units. The outdoor unit needs to be properly placed and secured, and the refrigerant lines must be properly connected. Additionally, electrical connections need to be made to ensure the heat pump functions effectively and efficiently.
On the other hand, an air conditioner typically only requires the installation of an indoor cooling unit. This can be a relatively simple process, as long as there is a suitable location for the unit and the necessary electrical connections are in place.
It’s important to note that the installation requirements may vary depending on the specific model and brand of heat pump or air conditioner. It’s always recommended to consult with a professional HVAC technician to ensure proper installation and optimal performance.
Cost Comparison
When considering whether to choose a heat pump or air conditioner for your home cooling solution, it is important to understand the key differences in terms of cost. While both options have their advantages and disadvantages, the cost factor can play a significant role in your decision-making process.
A heat pump is generally more expensive to install compared to an air conditioner. This is because heat pumps offer the additional functionality of both cooling and heating, which requires more complex equipment and installation. On the other hand, an air conditioner is designed solely for cooling purposes, making it a simpler and more affordable option.
However, it is important to consider the long-term cost savings when comparing a heat pump and air conditioner. Heat pumps are known for their energy efficiency, as they transfer heat instead of generating heat. This means that they can provide both cooling and heating functions at a lower cost compared to using separate systems for each. Over time, the energy savings from a heat pump can potentially offset the higher upfront installation cost.
Additionally, heat pumps can be eligible for government incentives and tax credits due to their energy-saving features. These financial incentives can help reduce the overall cost of installing a heat pump and make it a more financially attractive option in the long run.
In summary, while the upfront cost of a heat pump may be higher compared to an air conditioner, it is important to consider the long-term cost savings and potential financial incentives. Understanding the key differences in cost between the two options can ultimately help you make an informed decision for your home cooling solution.
Maintenance and Lifespan
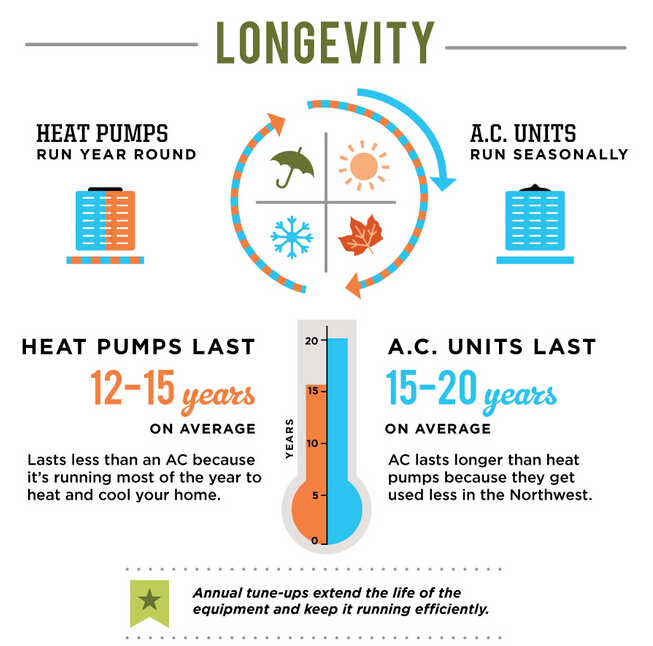
Understanding the key differences between a heat pump and an air conditioner is essential when it comes to their maintenance and lifespan. Both of these cooling solutions require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance and increased lifespan.
A heat pump, being a two-in-one system for heating and cooling, requires year-round maintenance. This includes regularly cleaning or replacing the air filters, checking and cleaning the outdoor unit, inspecting and lubricating the fan motor, and ensuring proper refrigerant levels. It is recommended to have a professional HVAC technician perform annual maintenance to keep the heat pump in top condition.
On the other hand, air conditioners are designed specifically for cooling and do not require year-round maintenance like heat pumps. The maintenance tasks for an air conditioner typically involve cleaning or replacing the air filters, cleaning the condenser coils, and checking the refrigerant levels. Regular maintenance, usually performed once a year, helps to ensure efficient cooling and extend the lifespan of the unit.
In terms of lifespan, air conditioners generally have a shorter lifespan compared to heat pumps. On average, an air conditioner can last anywhere from 10 to 15 years, while a well-maintained heat pump can last 15 to 20 years or even longer. The lifespan of both systems can be affected by factors such as usage, maintenance, and environmental conditions.
Ultimately, proper maintenance is crucial for both heat pumps and air conditioners to ensure optimal performance and longevity. Regular maintenance by a professional HVAC technician will help keep either system running efficiently and extend their lifespan, allowing for years of cool comfort in your home.
Noise Level
Understanding the noise level of your cooling solution is important when deciding between a heat pump and an air conditioner. Both options have key differences in noise levels that may impact your comfort and living environment.
A heat pump operates by transferring heat energy from the outside to the inside of your home, allowing it to provide both cooling and heating functions. Due to its design and components, a heat pump typically produces less noise compared to an air conditioner. This can be beneficial if you value a quieter cooling solution, especially if you plan to install the unit near living spaces or bedrooms.
An air conditioner, on the other hand, utilizes a different mechanism to cool the air inside your home. It relies on a compressor and refrigerant to remove heat from the air. As a result, air conditioners tend to generate more noise during operation. If noise level is a concern for you, it may be important to consider the location of the unit and its proximity to living areas.
When comparing the noise levels of a heat pump and an air conditioner, it’s essential to consider factors such as the specific models and brands, as well as the size and insulation of your home. Additionally, regular maintenance and cleaning of the cooling system can help minimize noise levels and ensure optimal performance.
Ultimately, understanding the noise level associated with each cooling solution will help you make an informed decision based on your preferences and the specific requirements of your home.
Aesthetics and Design
When it comes to the aesthetics and design of a cooling system, both heat pumps and air conditioners have their own unique features.
- Heat Pump: Heat pumps are typically larger in size compared to air conditioners. They often have an outdoor unit that houses the compressor and condenser, while the indoor unit contains the evaporator coil. Their design is usually more conspicuous, as they require visible outdoor components.
- Air Conditioner: Air conditioners are generally smaller and more compact in size compared to heat pumps. They usually consist of a single indoor unit that contains the evaporator coil and a compressor that is typically located outside the building. Due to their smaller size, they are often considered more aesthetically pleasing and less obtrusive.
Understanding the key differences in the aesthetics and design of heat pumps and air conditioners can help you make an informed decision when choosing the right cooling solution for your home. Consider factors such as available space, visual impact, and your personal preferences to determine which option fits best with your desired aesthetic.
Environmental Impact
Understanding the environmental impact of your cooling solution is crucial when deciding between a heat pump and an air conditioner. Both options have their differences in terms of their effect on the environment.
An air conditioner uses refrigerants that are known for depleting the ozone layer and contributing to global warming. These synthetic refrigerants, such as hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs) and hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), have a high global warming potential (GWP) and can remain in the atmosphere for many years.
In contrast, a heat pump is designed to transfer heat from one location to another, rather than using electricity to generate cold air like an air conditioner. This makes heat pumps a more energy-efficient cooling solution, resulting in lower carbon emissions and reduced electricity consumption. Furthermore, heat pumps can also be used for heating, making them a versatile and environmentally friendly choice.
Overall, the key environmental difference between a heat pump and an air conditioner lies in their use of refrigerants and their energy efficiency. Heat pumps have a smaller environmental footprint due to their use of more eco-friendly refrigerants and their ability to provide both cooling and heating functions.
Versatility and Additional Features
One of the main differences between a heat pump and an air conditioner is their versatility and additional features. While both systems are designed to cool your home, heat pumps have the advantage of being able to provide both cooling and heating functions. This means that a heat pump can be used as a year-round solution for your home’s temperature control needs.
Understanding this difference is important when considering your home cooling solution. If you live in a region with moderate climate conditions where both cooling and heating are needed, a heat pump can be a cost-effective and energy-efficient choice. It eliminates the need for separate heating systems, saving you money and reducing your carbon footprint.
On the other hand, air conditioners are designed solely for cooling purposes. They are typically less expensive to purchase and install compared to heat pumps. However, if you live in an area with cold winters, you will also need a separate heating system to keep your home warm.
In addition to their cooling and heating capabilities, heat pumps often have additional features that can enhance your comfort and convenience. Many modern heat pumps come with programmable thermostats that allow you to set different temperature schedules for different times of the day. Some models may also have smart home integration, allowing you to control your heat pump remotely using your smartphone or voice commands.
Air conditioners, on the other hand, may offer features such as multiple fan speed settings, adjustable louvers to direct airflow, and sleep mode for quieter operation during the night.
When choosing between a heat pump and an air conditioner, it is important to consider your specific needs and climate conditions. While both systems can effectively cool your home, a heat pump offers the added advantage of providing heating capabilities and additional features that can enhance your comfort and convenience.
Long-term Cost Savings
Understanding the key differences between a heat pump and an air conditioner is crucial when considering the long-term cost savings.
One of the main differences is in how these two systems operate. A heat pump works by transferring heat from one place to another, while an air conditioner simply removes heat from the indoor air. This means that a heat pump can provide both heating and cooling functions, whereas an air conditioner is only capable of cooling.
Due to its dual-functionality, a heat pump offers significant cost savings in the long run. With a heat pump, you can use the same system to cool your home in the summer and heat it in the winter, eliminating the need for separate heating and cooling systems. This results in lower upfront installation costs and reduced maintenance expenses over time.
In addition to the savings on equipment and maintenance, a heat pump also provides energy efficiency advantages. Heat pumps are designed to use less electricity than other heating and cooling systems. This is because they don’t have to generate heat or cool air, but rather transfer it from one location to another. As a result, heat pumps can help you save on energy bills over the lifespan of the system.
In summary, a heat pump offers long-term cost savings compared to an air conditioner due to its dual-functionality, reduced installation and maintenance costs, and energy efficiency advantages.
Professional Recommendation and Consultation
When it comes to choosing between a heat pump and an air conditioner, it is important to seek professional recommendation and consultation to ensure you make an informed decision. A professional understanding of the key differences between the two cooling solutions can help you determine which one is best suited for your needs.
An air conditioner operates by extracting heat from the air inside your home and expelling it outside, resulting in a cool indoor environment. On the other hand, a heat pump can both cool and heat your home by transferring heat from one place to another, depending on the season.
By consulting with a professional, you can gain a comprehensive understanding of the key differences between a heat pump and an air conditioner. They will take into account various factors such as your climate, energy efficiency goals, and budget to recommend the most suitable cooling solution for your home.
A professional consultation will also involve assessing your home’s insulation, size, and layout to determine the ideal cooling capacity required. This ensures that the recommended solution will effectively cool your space without unnecessary energy consumption.
Furthermore, a professional consultation will help you consider long-term costs and benefits. While heat pumps may require a higher initial investment, they can provide significant energy savings in the long run, especially in climates where both heating and cooling are needed.
In summary, seeking professional recommendation and consultation is crucial for understanding the key differences between a heat pump and an air conditioner. It allows you to make an informed decision based on your specific needs, climate, and budget. By considering factors such as energy efficiency, cooling capacity, and long-term costs, a professional can help you choose the most suitable cooling solution for your home.
Q&A:
What is the difference between a heat pump and an air conditioner?
A heat pump is a versatile device that can both cool and heat a home, while an air conditioner only cools.
Which is more energy-efficient, a heat pump or an air conditioner?
A heat pump is more energy-efficient than an air conditioner because it transfers heat instead of generating it, thus requiring less electricity.
Can a heat pump be used in colder climates?
Yes, a heat pump can be used in colder climates because it can extract heat from the outside air, even in low temperatures.
Do heat pumps require additional equipment for heating?
No, heat pumps do not require additional equipment for heating. They can simply reverse their operation to provide heat instead of cooling.
Are heat pumps more expensive than air conditioners?
Heat pumps may have a higher upfront cost than air conditioners, but their energy efficiency can result in long-term savings on utility bills.
What is a heat pump? How does it work?
A heat pump is a cooling and heating system that is designed to transfer heat from one area to another. It works by extracting heat from the outside air and transferring it inside during the winter months and vice versa during the summer months.
What is an air conditioner? How is it different from a heat pump?
An air conditioner is a cooling system that works by removing heat from the air inside your home and blowing it outside. The key difference between an air conditioner and a heat pump is that a heat pump can both cool and heat your home, while an air conditioner can only cool.






